Leave Your Message
The Solar Heat Pump industry is experiencing rapid growth, with a market value projected to exceed $9 billion by 2025. This technology harnesses solar energy for heating and cooling, making it an eco-friendly alternative for households and businesses. As stated by Dr. Emily Watson, a leading expert in renewable energy, “Solar Heat Pumps represent the future of sustainable energy solutions.”
Integrating solar heat pumps can significantly reduce energy costs. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), these systems can cut energy bills by up to 70%. However, there are challenges. Not all regions have consistent sunlight, which can impact efficiency. Furthermore, the initial installation costs can deter many potential users.
Despite these challenges, innovation continues to push the Solar Heat Pump market forward. Research indicates that advancements in technology could improve efficiency by 20% in the next five years. The shift toward clean energy is necessary, yet it also reveals a need for further education and infrastructure support. Thus, while the industry is promising, critical reflections on its implementation are essential for broader adoption.

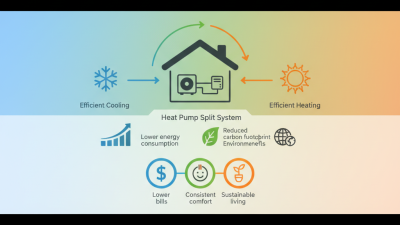
A solar heat pump is a device that combines solar energy with heat pump technology. It extracts heat from the environment to provide heating and hot water. Essentially, it works by using a refrigerant cycle. The system absorbs heat from ambient air, ground, or water, then compresses this heat for higher temperatures. The efficiency of solar heat pumps can be impressive. Reports indicate a coefficient of performance (COP) often exceeding 4.0. This means for every unit of electricity consumed, over four units of heat can be generated.
However, not all installations reach optimal performance. Factors like location, system size, and installation quality can greatly influence efficiency. The Climate Reality Project found that many systems underperform due to improper sizing for the building's heating needs. Additionally, regular maintenance is crucial. Data suggests that neglected systems can lose up to 30% efficiency over time. Therefore, careful planning and ongoing care are vital to harnessing the full potential of solar heat pumps. Embracing solar technology comes with its challenges, but the long-term benefits are significant.
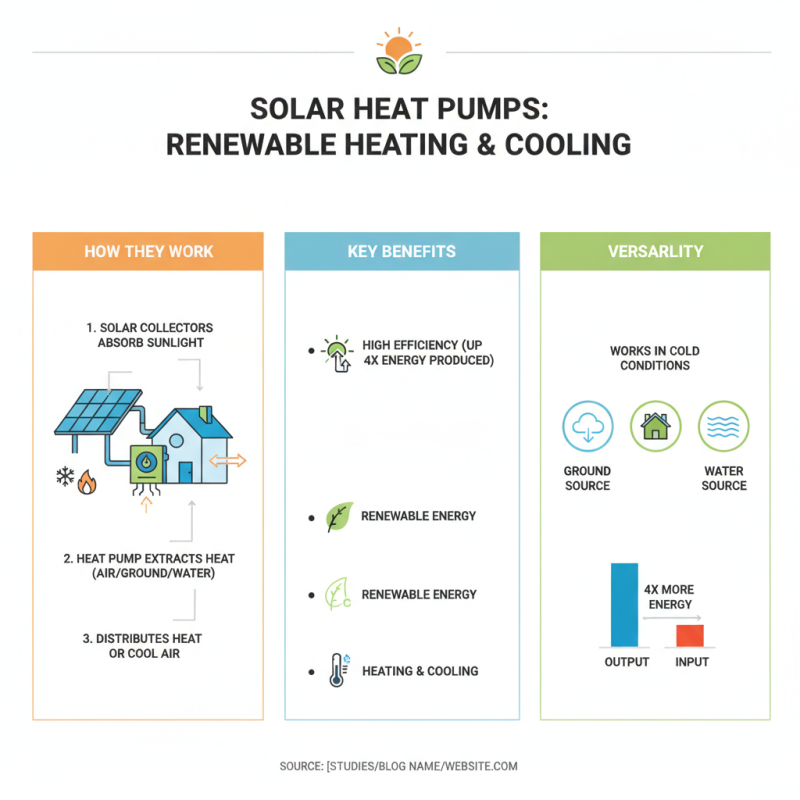
Solar heat pumps provide a unique solution for heating and cooling. They utilize renewable solar energy to enhance efficiency. By combining solar thermal collectors with a heat pump system, they can extract heat from the air, ground, or water even in colder conditions. Studies indicate that these systems can produce up to 4 times more energy than they consume, making them highly effective.
The operation of solar heat pumps hinges on a series of phases. Heat from the solar collectors is transferred to a refrigerant, which evaporates and then compresses. This process raises the temperature significantly. According to the International Energy Agency, using solar heat pumps can reduce carbon emissions by around 20%. However, systems can be complex and require careful installation. Maintenance is not always straightforward.
Performance varies based on location. For instance, in regions with inconsistent sunlight, the efficiency can drop. Research shows some systems function optimally when integrated with conventional heating sources. Understanding these nuances is crucial for maximizing performance. Testing different configurations can lead to better energy savings.
Solar heat pumps are an innovative technology that harnesses solar energy for heating. These systems comprise several key components that work together to convert solar energy into heat. The primary component is the solar collector, which captures sunlight and transfers it to a heat transfer fluid. This fluid is then pumped to a heat exchanger, where the heat is transferred to the indoor space or water.
Another important element is the heat pump itself. It amplifies the captured heat and circulates it through the building. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, these systems can achieve a coefficient of performance (COP) of 3 to 5, meaning they can generate three to five units of heat for every unit of electricity consumed. Despite their efficiency, installation costs can be a concern for many homeowners. The initial investment may seem high, but long-term savings on energy bills often justify it.
Lastly, a backup energy source is often needed. On cloudy days, the sun's energy may be insufficient. This can lead to reliance on an auxiliary heating system, which may not align with sustainability goals. While solar heat pumps offer substantial benefits, it’s crucial to evaluate their performance and adaptability to specific climate conditions. These factors play a significant role in the overall effectiveness of solar heat pump systems.
Solar heat pumps are increasingly popular for sustainable heating. They utilize solar energy to enhance efficiency. The efficiency of a solar heat pump is often measured by its coefficient of performance (COP). This metric indicates how much heat is produced for each unit of electricity consumed. Typically, a higher COP reflects better performance.
In terms of environmental impact, solar heat pumps significantly reduce carbon emissions. They rely on renewable energy, which minimizes reliance on fossil fuels. However, the initial installation can be costly and complex. This presents a barrier for many homeowners. Long-term benefits make them an attractive option. It’s important to consider location and climate. Not all areas receive enough solar radiation to optimize performance.
Ultimately, solar heat pumps represent a promising energy solution. Their efficiency ratings are essential in assessing their effectiveness. Yet, ongoing research and development are vital. There is still room for improvement in technology and affordability. Balancing eco-friendliness and cost is a challenge.
Solar heat pumps are becoming increasingly popular in modern systems. They use renewable energy from the sun to heat and cool spaces. This dual-purpose functionality makes them versatile and efficient. By capturing sunlight, these systems can deliver hot water for residential use. This approach often reduces energy costs.
In various applications, solar heat pumps are enhancing sustainability. They are effective in heating swimming pools, providing comfort in homes, or even serving commercial buildings. Many users have noted the advantages of lower electricity bills. Yet, initial installation costs can be daunting for some. Additionally, the efficiency of these systems can vary based on location and sunlight exposure.
Real-world use cases show mixed results. While many enjoy energy savings, others find performance falls short during cloudy days. Maintenance is another aspect to consider. Neglecting regular checkups can lead to decreased efficiency. Users should weigh factors carefully before investing in solar heat pumps to achieve their desired results.
| Dimension | Data |
|---|---|
| Heat Pump Type | Air Source, Ground Source, Water Source |
| Typical COP (Coefficient of Performance) | 3.0 to 5.0 |
| Annual Energy Savings | 25% to 50% |
| Application Areas | Residential Heating, Swimming Pools, Industrial Heating |
| Environmental Benefits | Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Enhanced Energy Efficiency |
| Installation Cost Range | $10,000 to $30,000 |
| Lifespan | 15 to 25 years |
| Maintenance Frequency | Annually |