Leave Your Message
Are you considering heating solutions for your home? A Heat Pump Heater might be the answer. These systems provide efficient heating and cooling, using the environment’s energy. They draw heat from the air or ground, making them eco-friendly.
Many homeowners appreciate their flexibility. A Heat Pump Heater can work in both summer and winter, offering year-round comfort. However, some may find initial installation costs high. It’s true that these systems can be a significant investment.
Yet, thinking long-term is crucial. They can lower energy bills significantly over time. With rising utility costs, a Heat Pump Heater offers a sustainable option. It’s worth examining the potential benefits and challenges to decide if it fits your lifestyle.

When considering heating options for your home, heat pump heaters stand out. They operate by transferring heat instead of generating it. This makes them highly energy-efficient, lowering utility bills. Compared to traditional heaters, they use less electricity. This translates to cost savings over time, which is appealing for many homeowners.
Heat pumps also provide consistent warmth. They maintain a steady temperature, unlike some traditional systems that fluctuate. This can enhance comfort levels significantly. Additionally, heat pumps can also cool your home in the summer, offering year-round climate control. However, some homeowners worry about their performance in extreme cold. It’s essential to assess your regional climate before deciding.
Another factor to consider is installation requirements. Heat pumps can sometimes need more upfront investment. Installation may involve new ductwork or system modifications. While this might seem daunting, the long-term savings and efficiency often outweigh these initial challenges. Ultimately, understanding these nuances is crucial when evaluating options for your home heating needs.
When considering a heat pump heater for your home, energy efficiency is key. Heat pumps use less energy than traditional heating systems. They extract heat from the air, ground, or water. This process consumes less electricity. The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) are critical metrics. They measure how efficiently the system operates over an entire season.
Comparing these ratings can be revealing. A higher SEER indicates better cooling efficiency. A higher HSPF shows effective heating in colder months. These metrics help homeowners choose wisely. It’s important to note that actual performance can vary. Environmental factors and system installation play roles. A unit may not reach its rated efficiency if improperly installed.
Some heat pumps may struggle in extreme temperatures. They can become less efficient when it's very cold outside. Homeowners should think about this before buying. Researching specific models is essential. Balancing efficiency with your home's unique needs can be challenging. Making the right choice requires careful thought and consideration.
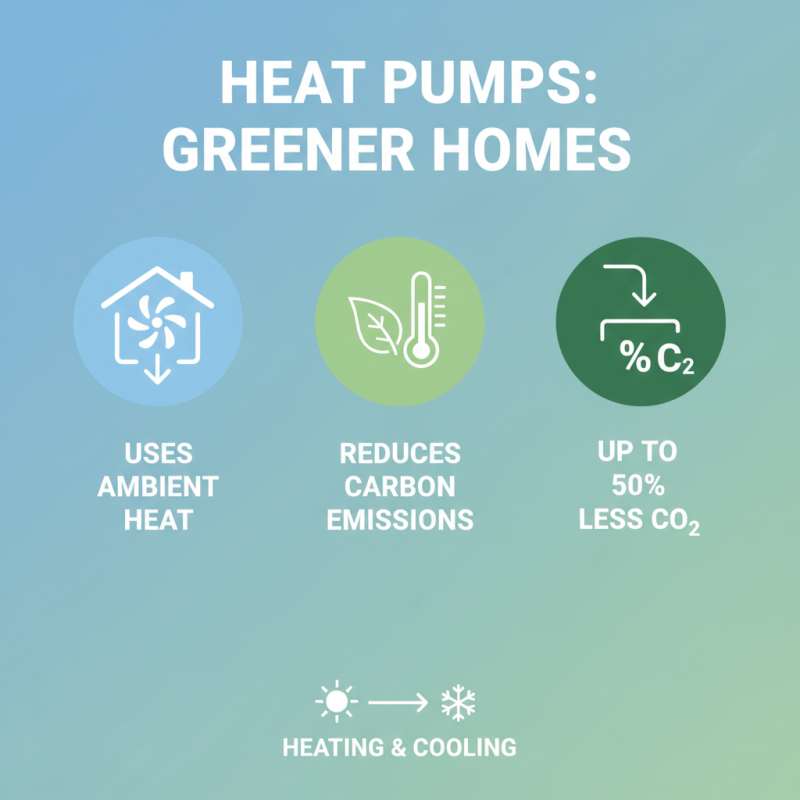
Heat pumps are gaining attention for their positive environmental impact. They utilize ambient air or ground sources to provide heating and cooling. This process significantly reduces carbon emissions compared to traditional heating systems. In fact, heat pumps can lower a home's carbon footprint by up to 50%. They do this by transferring heat rather than generating it through combustion.
The efficiency of heat pumps is notable. They convert one unit of electricity into several units of heating or cooling. This process means less energy consumption overall. However, it’s important to recognize that the environmental benefits can vary based on the electricity source. If powered by fossil fuels, the impact isn't as significant. Using renewable energy enhances the environmental advantages greatly.
The transition to heat pumps isn’t without its challenges. Installation costs may be higher than expected. Some homeowners might find the technology overwhelming. Nevertheless, the long-term savings on energy bills can justify the initial investment. Every choice we make has its consequences. Transitioning to heat pumps is a step toward reducing our collective carbon footprint. It's essential to consider all aspects of this decision thoughtfully.
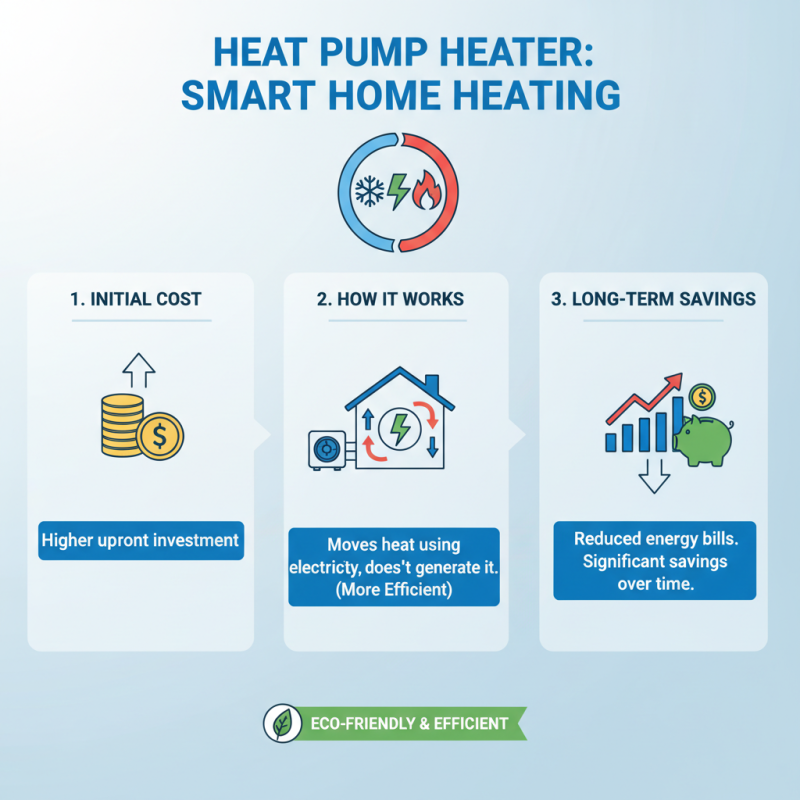
When considering home heating options, a heat pump heater stands out for its efficiency. The initial installation cost may seem high, but the long-term savings can be significant. By using electricity to move heat rather than generating it, these systems reduce energy consumption. home and reflected on energy expenses.
In colder months, heat pump heaters can still be effective due to their ability to draw heat from the outside air. This can lower heating bills by up to 50% compared to traditional systems. However, it’s essential to consider climate factors, as performance may decrease significantly in extreme cold. Homeowners must evaluate their local conditions and energy prices.
Investing in a heat pump heater could yield a return in less than five years. Over time, maintenance costs can also be lower than those for conventional heaters. Still, making the switch requires careful thought. It’s crucial to analyze your home’s unique needs before proceeding with installation.
The evolution of heat pumps has brought significant technological advancements. Modern heat pump designs now include variable speed compressors. This allows for better temperature control and energy efficiency. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, heat pumps can reduce energy consumption by up to 50% compared to traditional heating systems. This is particularly appealing in regions with fluctuating climates.
Innovations such as enhanced refrigerants and smart controls are improving performance. New refrigerants have a lower global warming potential. They help meet environmental regulations while enhancing efficiency. Smart controls allow users to monitor and adjust settings remotely, optimizing energy usage. Yet, some homeowners struggle to fully utilize these features. Many remain unaware of smart technology's benefits. Regular maintenance is also crucial to keeping systems running efficiently.
Despite numerous advancements, challenges persist in the heat pump market. Installation costs can be high, deterring potential users. Homeowners might also face difficulties in selecting the right system for their needs. Education about heat pumps and available technologies remains limited. Industry stakeholders must address these gaps to encourage broader adoption. This will ensure that more homes can harness the benefits of heat pump heating technologies.






